Sociodemographic, clinical and pathological characteristics associated with urinary tract infection in diabetics: case and control study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36393/spmi.v32i1.15Keywords:
Diabetes, risk factor, UTIAbstract
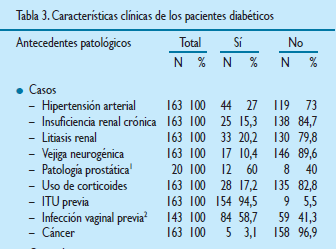
Objective. To determine which sociodemographic characteristics, clinical and pathological antecedents constitute a greater risk to have urinary tractinfection (UTI), according to the case-control study, in type 2 diabetic population. Material and MethOds. comparative, cross-sectional, retrospective study and explanatory, performed in the Internal medicine service of Loayza Hospital in 2016. Charts of 163 diabetic patients with UTI and 163 diabetics without UTI were reviewed. Chi square was initially applied and then logistic regression with Wald statistic for multivariate analysis. results. The sociodemographic characteristics have no statistical relationship with the occurrence of UTI (p > 0,05). Disease time ≥ 10 years (OR = 3,978 (95%CI 1,467-10,790), p = 0,007), Chronic renal failure (OR = 8,412 (95%CI 1,832-38,615), p = 0,006), Kidney lithiasis (OR= 10,604 (95%CI 2,144-52,459), p = 0,004), neurogenic bladder (OR= 12,290 (95%CI 1,447-104,386), p = 0,022), corticosteroid use (OR= 17,850 (95%CI 3,789-84,087), p = 0,000), previous
UTI (OR = 27,757 (95%CI 9,280-83,027), p = 0,000) and present vaginal infection or prostatic pathology (OR = 4,958 (95%CI 2,149-11,439), p = 0,000) were independently associated with the occurrence of ITUs.
COnClusiOns. Sociodemographic characteristics have no statistical relationship with UTI. Disease time > = 10 years, chronic renal failure, renal lithiasis, neurogenic bladder, use of corticosteroids, previous UTI and presenting vaginal infection or prostatic pathology are statistically associated with the occurrence of UTI in type 2 diabetic population.
Downloads